| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- ADsP
- scikit learn
- 딥러닝
- 이것이 코딩테스트다
- pytorch
- 태블로
- 데이터 전처리
- 이코테
- 머신러닝
- matplotlib
- tableau
- 자격증
- 파이썬
- 데이터분석준전문가
- IRIS
- 시각화
- r
- 회귀분석
- SQL
- 데이터 분석
- Deep Learning Specialization
- sklearn
- pandas
- Google ML Bootcamp
- 통계
- Python
- ML
- SQLD
- 코딩테스트
- 데이터분석
- Today
- Total
함께하는 데이터 분석
[Find-A][Scikit Learn] Decision Tree 본문
의사결정 나무(Decision Tree)
- 분류와 회귀 작업, 다중출력 작업도 가능한 다재다능한 머신러닝 알고리즘
- 최근에 자주 사용되는 강력한 머신러닝 알고리즘 중 하나인 랜덤 포레스트의 기본 구성 요소
1. 의사결정 나무 학습과 시각화
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
iris = load_iris()
X = iris['data'][:, (2, 3)]
y = iris['target']사이킷런의 iris 데이터를 불러오고 X에 PetalLength, PetalWidth
y에 꽃의 품종인 Setona, Versicolor, Virginica를 할당
tree_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2, random_state=42)
tree_clf.fit(X, y)깊이를 2로 설정하고 시드 넘버를 42로 설정
import graphviz
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
tree = export_graphviz(tree_clf,
out_file = None, # file로 저장 여부
feature_names = iris.feature_names[2:], # feature 이름
class_names = iris.target_names, # target 이름
filled = True, # 그림에 색상 여부
rounded = True, # 반올림을 진행 여부
special_characters = True) # 특수문자를 사용 여부
graph = graphviz.Source(tree)
graph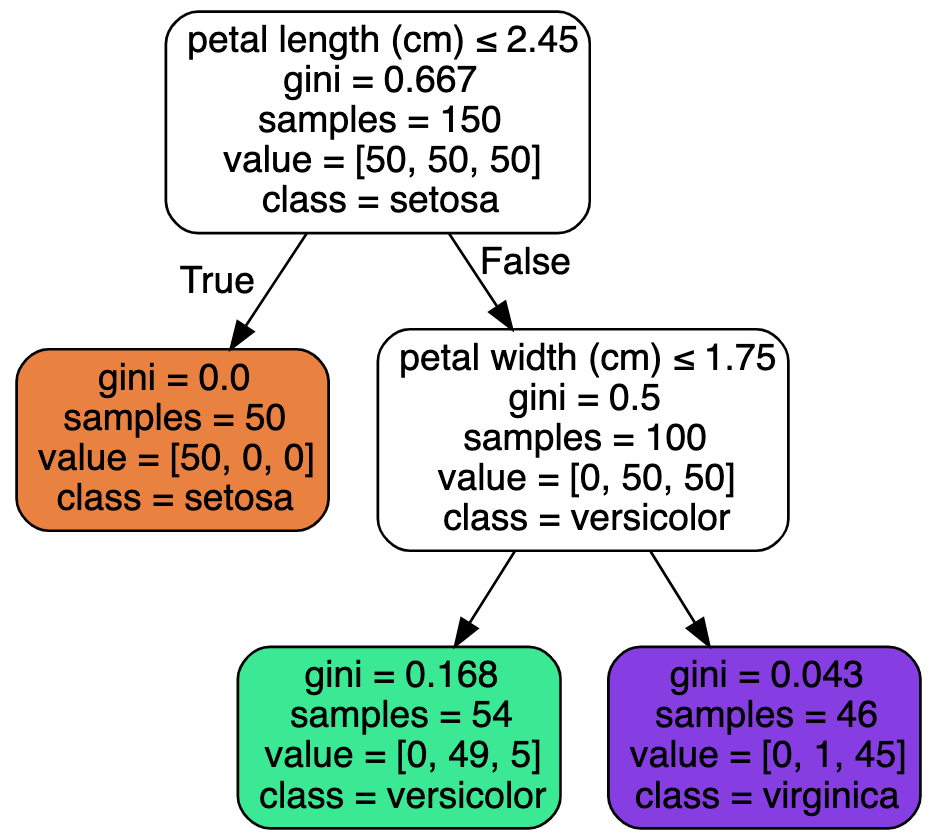
2. 예측하기
루트 노드에서 꽃잎의 길이가 2.45보다 짧거나 같은지 검사
짧다면 깊이가 1인 왼쪽의 자식 노드로 이동하고 Setona로 예측
이 경우 자식 노드를 가지지 않는 리프 노드이므로 추가적인 검사를 하지 않음
다른 꽃의 꽃잎의 길이가 2.45보다 길다면 오른쪽 자식 노드로 이동
이 노드는 자식을 갖고 리프 노드가 아니므로 꽃잎의 너비가 1.75보다 작은지 검사
작다면 Versicolor, 크다면 Virginica로 예측
노드의 value 속성은 노드에서 각 클래스의 훈련 샘플의 수를 나타냄
gini는 불순도(impurity)를 측정
0에 가까울수록 순수 노드 예를 들어 깊이 2의 왼쪽 노드의 gini점수는
1 - (0/54)^2 - (49/54)^2 - (5/54)^2 이므로 대략 0.168

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
def plot_decision_boundary(clf, X, y, axes=[0, 7.5, 0, 3], iris=True, legend=False, plot_training=True):
x1s = np.linspace(axes[0], axes[1], 100)
x2s = np.linspace(axes[2], axes[3], 100)
x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(x1s, x2s)
X_new = np.c_[x1.ravel(), x2.ravel()]
y_pred = clf.predict(X_new).reshape(x1.shape)
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#fafab0','#9898ff','#a0faa0'])
plt.contourf(x1, x2, y_pred, alpha=0.3, cmap=custom_cmap)
if not iris:
custom_cmap2 = ListedColormap(['#7d7d58','#4c4c7f','#507d50'])
plt.contour(x1, x2, y_pred, cmap=custom_cmap2, alpha=0.8)
if plot_training:
plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==0], X[:, 1][y==0], "yo", label="Iris-Setosa")
plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==1], X[:, 1][y==1], "bs", label="Iris-Versicolor")
plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==2], X[:, 1][y==2], "g^", label="Iris-Virginica")
plt.axis(axes)
if iris:
plt.xlabel("Petal length", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Petal width", fontsize=14)
else:
plt.xlabel(r"$x_1$", fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel(r"$x_2$", fontsize=18, rotation=0)
if legend:
plt.legend(loc="lower right", fontsize=14)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plot_decision_boundary(tree_clf, X, y)
plt.plot([2.45, 2.45], [0, 3], "k-", linewidth=2)
plt.plot([2.45, 7.5], [1.75, 1.75], "k--", linewidth=2)
plt.plot([4.95, 4.95], [0, 1.75], "k:", linewidth=2)
plt.plot([4.85, 4.85], [1.75, 3], "k:", linewidth=2)
plt.text(1.40, 1.0, "Depth=0", fontsize=15)
plt.text(3.2, 1.80, "Depth=1", fontsize=13)
plt.text(4.05, 0.5, "(Depth=2)", fontsize=11)
plt.show()
위의 사진은 의사결정 나무의 결정 경계를 나타냄
깊이 0인 루트 노드는 꽃잎의 길이 2.45가 기준이 됨
왼쪽 영역은 Setona만 있기에 더 나눌 수 없음
하지만 오른쪽 영역은 순수 노드가 아니므로 깊이 1의 오른쪽 노드는 꽃잎의 너비 1.75에서 나누어짐
3. 클래스 확률 추정
print(tree_clf.predict_proba([[5, 1.5]]))
>>> [[0. 0.90740741 0.09259259]]
print(tree_clf.predict([[5, 1.5]]))
>>> [1]의사결정 나무는 한 샘플이 특정 클래스 k에 속할 확률 추정 가능
길이가 5, 너비가 1.5인 꽃은 리프 노드는 깊이 2에서 왼쪽 노드
즉, Setona는 0%, Versicolor는 90.7%, Virginica는 9.3%이고
하나의 클래스를 예측한다면 가장 높은 확률을 가진 Versicolor를 출력
https://www.hanbit.co.kr/store/books/look.php?p_code=B9267655530
핸즈온 머신러닝
최근의 눈부신 혁신들로 딥러닝은 머신러닝 분야 전체를 뒤흔들고 있습니다. 이제 이 기술을 거의 모르는 프로그래머도 데이터로부터 학습하는 프로그램을 어렵지 않게 작성할 수 있습니다. 이
www.hanbit.co.kr
'학회 세션 > 파인드 알파' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Find-A] 인공 신경망 (0) | 2022.09.12 |
|---|---|
| [Find-A][Scikit Learn] 앙상블 학습 (0) | 2022.08.28 |
| [Find-A] [Scikit Learn] 소프트맥스 회귀 (0) | 2022.08.20 |
| [Find-A] [Scikit Learn] 로지스틱 회귀 (0) | 2022.08.19 |
| [Find-A] 파인드 알파 머신러닝이란? (1) | 2022.08.12 |




